Electronic Technology Forum
MOS integrated circuit system design examples and detailed logical structure
MOS integrated circuit system design examples
Take a desktop computer as an example to illustrate the design of a system composed of MOS integrated circuits.
Because the characteristics of MOS integrated circuits are consistent with the requirements of desktop computers for integrated circuits, both have been developed rapidly. The desktop computer example cited here is the simplest example to study the relationship between MOS integrated circuits and machine design.
Generally speaking, the design procedure of integrated circuit desktop computer is as follows.
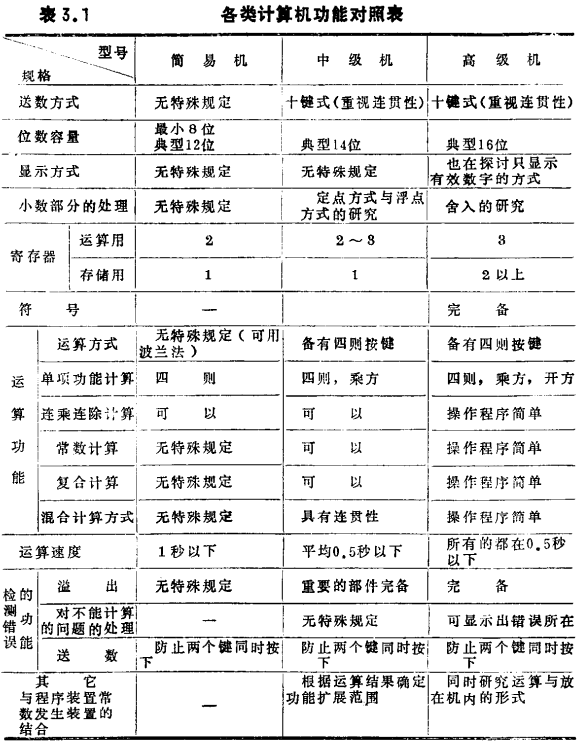
(1) Compile a list of computer functions of various levels, and determine the specifications of the machine according to the required functions (see Table 3.1).
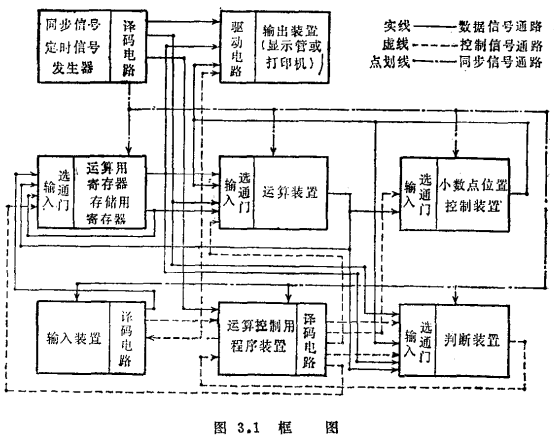
(2) Analyze the basic structure of the computer and make a block diagram of the electronic circuit part (see Figure 3.1).
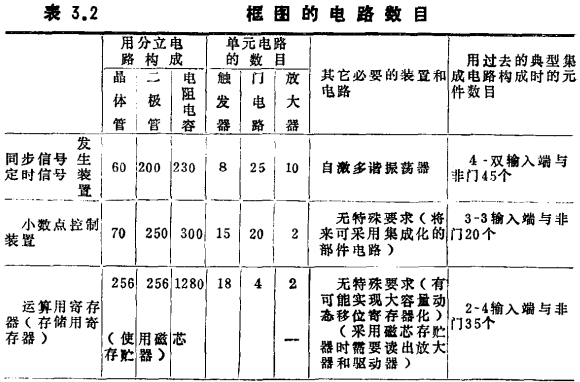
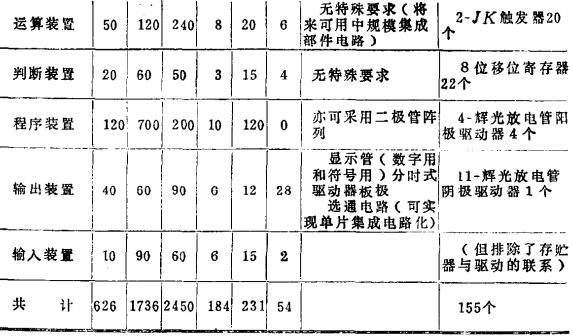
(3) Analyze the basic circuits in the block diagram, calculate the number of circuits required to form each block diagram, analyze the characteristics of each block diagram, and its connection with other block diagrams, and compile a list of block diagram composition (see Table 3.2).
After preparing these reference materials, select MOS integrated circuits suitable for the characteristics of each block diagram according to these reference materials, that is, adopt a certain method to design the structure of the logic circuit.
(1) Timing signal generating device
Desktop electronic computers generally adopt a logic circuit method based on a serial synchronous two-one decimal system, so there should be signals that generate and execute various beats, that is, synchronous signals and timing signals. Among them are: clock pulse ф, bit time signal ti, digital signal period Tj, word time signal and so on. These signals can be generated on the basis of a self-excited multivibrator with a coded counter and decoding circuit. However, considering the requirements of improving integration and flexibly adapting to changes in the number of bits, the ring counting method is mostly used.
(2) Decimal point control device
This is a device that stores and controls the position of the decimal point of a digital register. In addition and subtraction operations, it aligns the decimal point of the number to be added (subtracted) and the number of addition (subtraction); in multiplication and division, it can calculate the number of decimal places of the operand and the number of decimal places of the operand And (or difference). The position of the decimal point is most effectively expressed in the form of digitization of the number of decimal places, such as a 16-bit computer, which is composed of a serial synchronous pure binary addition and subtraction device that can handle a value of 0~±15. Of course, there is also a method of setting a special decimal point at the highest bit of the indexed digital register and using a digital arithmetic device to perform the above-mentioned arithmetic operations. However, when a medium-scale integrated circuit is used, the former circuit is conducive to concentrating this part into one device.
(3) Register for operation
It is composed of a serial synchronous shift register. The shift register is divided into dynamic type and static type, and can also be distinguished by operation mode. Its characteristic is that the number of input terminals is very small, which is very suitable for integrated circuit, and the internal circuit is simple, the power consumption is low, and the integration is easy to improve. In addition, in the case of a dynamic type, generally the feedback loop for successive storage and the gate circuit for exchanging new information are included, and the shift register system is made into an integrated circuit.
(4) Computing device
The arithmetic devices of a desktop computer can be roughly divided into a decimal addition and subtraction device for the four arithmetic calculations and a block calculation dedicated gate circuit group for square root calculations. The former is best made as a serial synchronous two-decimal adder and subtracter, using only positive logic signals to try to reduce the area of the entire system. The latter first considers the high degree of freedom and requires flexibility in making choices.
(5) Judging device
It is a device that detects the status of information. For example, it can determine whether the highest bit of the register is zero. The input signal is composed of the output signal of the information strobe circuit and the output signal of the comparison digital strobe circuit, and the device should be a coincidence detection circuit. This device is different from the above-mentioned devices and requires a higher degree of freedom.
(6) Programming device
The arithmetic operation of the desktop computer is to decompose each operation into the four basic operations of shift, addition and subtraction, transfer, and judgment, and combine and control these basic operations in an appropriate order. This kind of device that is combined in sequence and controlled by a program is a program device. Diode arrays and NAND gates can be used. However, it is generally required that the specifications should not be too rigid. The method of forming this part with a counter-type control device is not suitable for small-scale integrated circuits. However, when using large-scale integrated circuits, counter-type control devices can also be used to form this part of the circuit.
(7) Output device
The output device mostly uses a digital display tube, which will be discussed below. Because the digital storage registers are all serial synchronous, so the time-sharing method is generally used to select the electrodes of the digital display tube, and the output voltage of the serial register is only added to the display electrode at the initial time of each bit, that is, the display tube is used with the display tube. The corresponding display mode of the "bit" position value.
The following issues must be considered when making this device into an integrated circuit.
1) High withstand voltage switching circuit.
2) The combination of logic gate circuit and high withstand voltage switch circuit.
3) Take measures to prevent the destruction of each independent circuit.
(8) Input device
The input device of a desktop computer is a key switch, but when converting the output of such a key switch into an electronic signal, careful consideration should be given to the method of eliminating the influence of mechanical switch vibration, and the conversion of electronic signals synchronized with the computer should also be fully considered.
As mentioned above, MOS can only be used after fully analyzing the characteristics of the various components that constitute the desktop computer, the proportions of the components required by each device shown in Table 3.2, and the signal exchange relationship between the devices obtained from the block diagram in Figure 3.1. System design of integrated circuits. For reference, the rightmost column of Table 3.2 lists the component list when a typical integrated circuit is used. When using MOS integrated circuits, it is necessary to develop integrated circuits suitable for the MOS structure according to the requirements for facilitating function division, and try to improve the integration of the entire computer.
Contact: Mr. Zou
Contact number: 0755-83888366-8022
Mobile phone: 18123972950
QQ: 2880195519
Contact Address: 5C1, Block CD, Tianji Building, Tianan Digital City, Chegongmiao, Futian District, Shenzhen
Please search WeChat official account: "KIA Semiconductor" or scan the following picture to "Follow" official WeChat official account
Please "follow" the official WeChat account: provide MOS tube technical assistance



