Electronic Technology Forum
Switched capacitor full wave detector and peak detector circuit working principle
1. Full wave detector
A full-wave detector and a peak detector are constructed using switched capacitor circuits. The former transforms the input signal Vin(t) into its absolute value | Vin(t)|, and the latter detects the bee value of the input signal. A relatively simple full-wave detector is shown in Figure 6.4-3. When the input signal Vin>0, the output voltage of the op amp A1 is negative, M1 is off, and the switched capacitor circuit composed of capacitor 2C does not work. At this time, the circuit is in-phase amplification, and its gain is 1, that is, Vo(t) =Vin(t); when the input signal Vin<0, the output voltage of the op amp A1 is positive, M1 is turned on, the switched capacitor circuit formed by the capacitor 2C and the op amp A1 form an inverting amplifier, the gain is 2, and the capacitor The switched capacitor circuit formed by C and op amp A2 form in-phase amplification with a gain of 1. According to the superposition theorem, the transfer function of this circuit is Vo(t)/Vin(t)-1. As mentioned above, this circuit reverses the negative polarity signal, while the positive polarity signal is in phase, and the gain is equal to 1, thus achieving Full wave detection, namely Vo=lVinl.

2. Peak detector
The peak detector is a circuit that detects and maintains the maximum positive (or negative) voltage of the input signal. The relationship between its input and output is shown in Figure 6.4-5.

Figure 6.4-5 is a switched capacitor peak detector. The capacitor C in the figure stores the maximum value of Vin before this moment , The op amp A1 compares the current Vin value with
, The op amp A1 compares the current Vin value with Compare. If Vin>
Compare. If Vin> , The output of op amp A1 is negative; as ф1 and ф2 become high level, the logic output A is high level, so that the input switch M1 is turned on,
, The output of op amp A1 is negative; as ф1 and ф2 become high level, the logic output A is high level, so that the input switch M1 is turned on, charge the capacitor C so that the voltage across the capacitor C is the maximum value of the Vin signal. If Vin>
charge the capacitor C so that the voltage across the capacitor C is the maximum value of the Vin signal. If Vin> , Then the logic output A is low level, the M1 tube is cut off, and the output voltage
, Then the logic output A is low level, the M1 tube is cut off, and the output voltage (That is, the voltage across the output signal of the capacitor C) continues to remain at
(That is, the voltage across the output signal of the capacitor C) continues to remain at 。
。
When ф1=1 (high level), Vin and
Perform comparison; when ф2=1, the capacitor C is charged, therefore, there is a time delay between comparison and charging. If the clock frequency is greater than the highest frequency of Vin, the error caused by the delay between comparison and charging Can be ignored.
A buffer is usually added to the output (as shown in Figure 6.4-5, unity gain op amp A2) to prevent capacitor C from discharging.
The continuous-time peak detector is shown in Figure 6.4-6, in which op amp A is used as a comparator. If Vin and
 ,The output of the op amp goes high. M1 is turned on, C is charged, so that
,The output of the op amp goes high. M1 is turned on, C is charged, so that
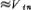 ,If Vin
,If Vin , The output of the op amp becomes low level, M1 is cut off, and C remains
, The output of the op amp becomes low level, M1 is cut off, and C remains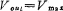 . Similarly, if the output needs to drive a load, a buffer stage must be added.
. Similarly, if the output needs to drive a load, a buffer stage must be added.

Contact: Mr. Zou
Contact number: 0755-83888366-8022
Mobile phone: 18123972950
QQ: 2880195519
Contact Address: 5C1, Block CD, Tianji Building, Tianan Digital City, Chegongmiao, Futian District, Shenzhen
Please search WeChat official account: "KIA Semiconductor" or scan the following picture to "Follow" official WeChat official account
Please "follow" the official WeChat account: provide MOS tube technical assistance




