Electronic Technology Forum
Detailed explanation of MOS field effect transistor threshold voltage temperature effect
In order to make the MOS field effect tube work stably and reliably within a certain temperature range, the design must consider adapting its parameters to changes with temperature. There are two general operating temperature ranges for semiconductor devices: one is the military range, usually -55~+125℃; the other is One is the civil range, generally -25~85℃. MOS tube threshold voltage temperature effect. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the requirements for the temperature performance of the field effect tube according to different usage conditions.
The change of MOS field effect tube performance with temperature is mainly manifested in the threshold voltage VTand the change of carrier mobility with temperature are discussed separately below.
1. Threshold voltage VT changes with temperature
Take the n-channel enhanced tube as an example for discussion. From the discussion in Section 2, we can see that the turn-on voltage of the n-channel enhanced tube (see (1.2-12) The formula and its description) is
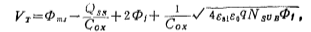
式中
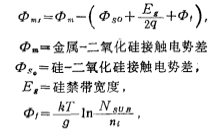
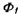 is Fermi potential of p-type substrate, where the relationship between
is Fermi potential of p-type substrate, where the relationship between 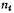 and T Can be expressed as
and T Can be expressed as
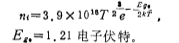
Assuming that the positive charge surface density Qss in the oxide layer has nothing to do with the temperature T, the experiment also found that SiO2 The contact potential difference between the metal on both sides and the semiconductor Si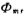 , in a very wide Within the temperature range, it is approximately independent of temperature. MOS tube threshold voltage temperature effect. In this way, we can get the rate of change of VT with temperature T
, in a very wide Within the temperature range, it is approximately independent of temperature. MOS tube threshold voltage temperature effect. In this way, we can get the rate of change of VT with temperature T
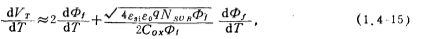
where
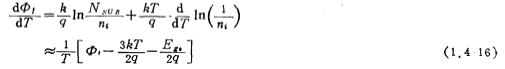
If T=300K, 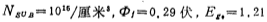 Electron volt, tox=1000 angstroms, Cox=35×10-3 law, then there is< /span>
Electron volt, tox=1000 angstroms, Cox=35×10-3 law, then there is< /span>
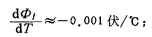
If
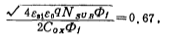
then
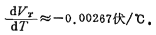
The calculated turn-on voltage changes with temperature are more consistent with the experimental results. Therefore, for the above example, if the operating temperature change range is ΔT =+100℃, then em>ΔVT≈ - 0.267 volts; if At 25℃, VTis1 volt; at 125℃, VT is 0.733 volts, such asFigure 1.4-5 as shown. MOS tube threshold voltage temperature effect. For the Hegou MOS tube, when the temperature increases, the threshold voltage will decrease. For the P-channel MOS tube, the same discussion can be done. Its 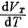 total It is a positive value. Figure 1.4-5 shows how the threshold voltage VT changes with temperature for the n-channel MOS tube.
total It is a positive value. Figure 1.4-5 shows how the threshold voltage VT changes with temperature for the n-channel MOS tube.
2. The change of carrier mobility with temperature
The change of carrier mobility in the channel with temperature is the second important factor in the temperature effect of MOS field effect transistors. ActualVerify that, for MOS FET, if the surface electric field is less than 10 2V/cm, the effective mobility of electrons and holes in the channel is approximately constant, and approximately equal to half of the mobility in the semiconductor body. Experiments have found that in the temperature range of -55~+125℃, the mobility μ is approximately inversely proportional to the temperature T, that is

3. Drain-source current IDS changes with temperature
The threshold voltage of the MOS tube and the mobility of the relatively current with the temperature will in turn affect the conductance of the MOS tube, that is, its current.
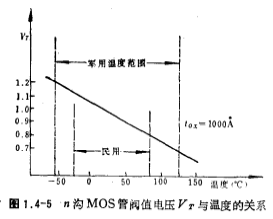
The reduction of VT makes I< /span>DS increases, μn decreases IDS decreases, so when the temperature rises, IDS Whether to increase or decrease depends on which of these two effects play the main role. For this reason, the (1.3-9) formula is used to find the derivative of T
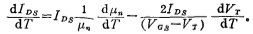
Because within the general operating temperature range , so the above formula becomes
, so the above formula becomes
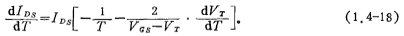
If the turn-on voltage of an n-channel MOS FET is VT=1V: VGS=3V,  Volt/℃, then
Volt/℃, then 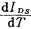 The value at 300K
The value at 300K
Contact: Mr. Zou
Contact number: 0755-83888366-8022
Mobile phone: 18123972950
QQ: 2880195519
Contact Address: 5C1, Block CD, Tianji Building, Tianan Digital City, Chegongmiao, Futian District, Shenzhen
Please search WeChat official account: "KIA Semiconductor" or scan the following picture to "Follow" official WeChat official account
Please "follow" the official WeChat account: provide MOS tube technical assistance